Over the past decade, account ownership across sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) has surged, driven by the widespread adoption of mobile money, a key factor accelerating financial inclusion, according to the World Bank’s latest global Findex 2025 report, titled “Connectivity and Financial Inclusion in the Digital Economy.”
In SSA (excluding high-income countries), 58.2% of adults aged 15 and above now own an account with a bank, mobile money provider, or similar financial institution—up from 49.3% in 2021 and more than double the 23.3% recorded in 2011, when the first round of findex data was collected.
“Mobile money accounts are driving this growth in account ownership,” the report said. “More than half of all accounts in low- and middle-income economies are now digitally enabled through mobile phones or payment cards.”
The World Bank’s findings align with the GSMA’s State of the Industry Report on Mobile Money, which reveals that Africa now accounts for over 1.1 billion registered mobile money accounts—more than half of the world’s total—up from 395.7 million in 2019.
According to the multilateral lender, the region remains the global leader in mobile money adoption, with 40% of adults owning a mobile money account in 2024, up from 27% in 2021
Other regions are catching up, particularly Latin America and the Caribbean, where mobile money adoption rose to 37%, and parts of Europe and Central Asia are also closing the gap through digital innovation.
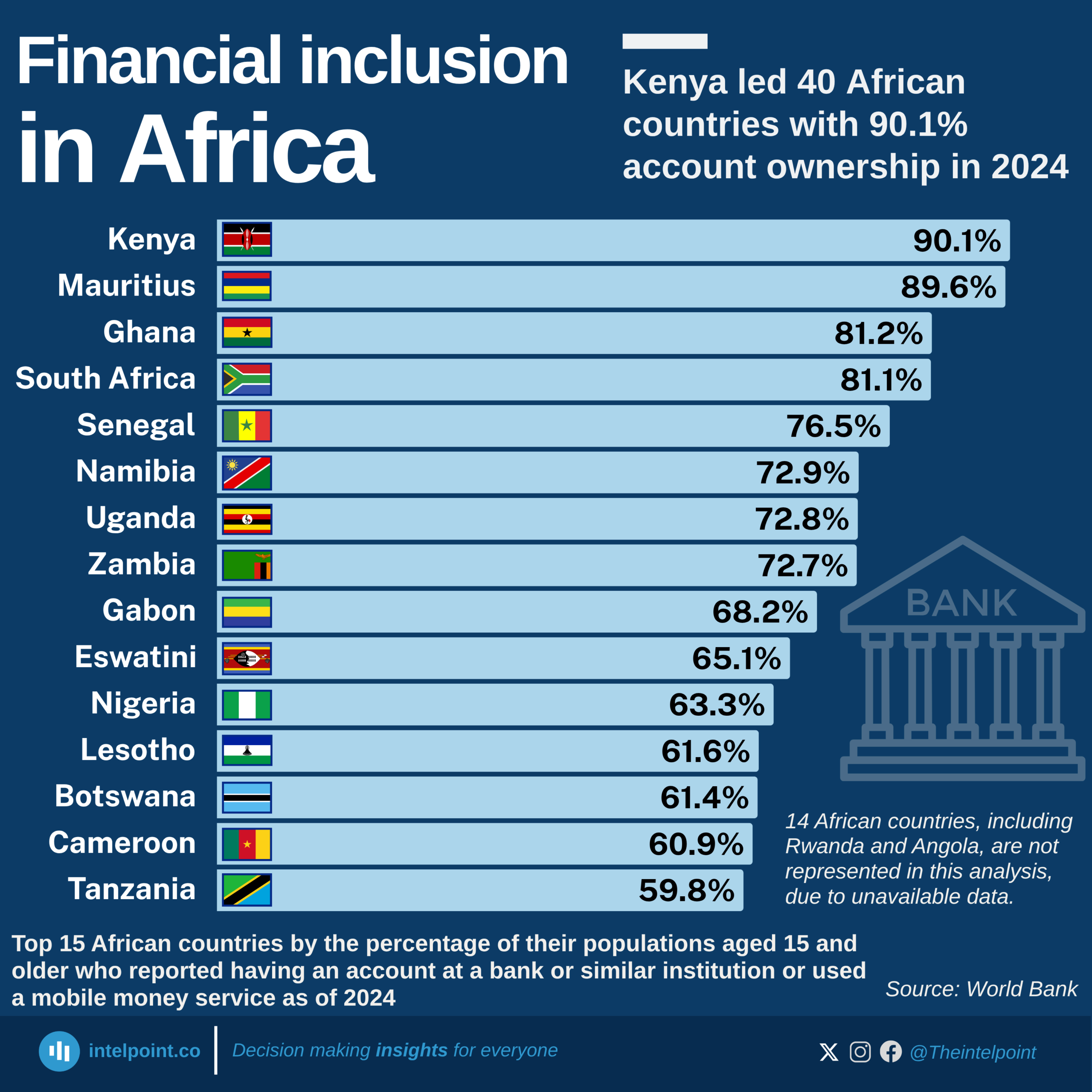
SSA countries with the highest banked population
Kenya – 90.1%
Kenya leads SSA in account ownership, overtaking Mauritius. Its rapid rise—from 79.1% in 2021—is attributed to deep mobile money penetration via platforms like M-Pesa and Airtel Money. Nearly every adult (93%) owns a mobile phone, and 60% accessed the internet recently—a staggering 89% of adults made or received digital payments in 2024.
Mauritius – 89.6%
Mauritius closely follows, though it slipped slightly from 90.5% in 2021. With strong digital infrastructure, 94% mobile phone ownership, and 77% internet usage, the country boasts a solid savings culture. However, only 32% of adults saved formally in 2024, and 19% borrowed, indicating moderate engagement with credit services.
Ghana – 81.2%
Ghana made significant progress, jumping from 68.2% in 2021. Government-led digitisation and widespread mobile wallet use fueled this growth. Notably, 80% of adults made or received digital payments in 2024, and 67% saved formally. Mobile phone ownership stands at 88%.
South Africa – 81.1%
Despite slipping from 85.4% in 2021, South Africa remains a financial powerhouse. It boasts Africa’s most advanced banking infrastructure. In 2024, 67% of adults made digital payments, 36% saved formally, and 13% borrowed. Mobile phone (87%) and internet usage (68%) remain strong.
Senegal – 76.5%
Senegal made a 21-point leap from 56% in 2021, driven by improved mobile access and digital inclusion for women and rural communities. In 2024, 73% of adults made digital payments, and 58% saved formally. Mobile phone ownership stands at 87%, with 70% internet usage.
Namibia – 72.9%
Up from 71.3%, Namibia maintains a steady level of digital payment use (68%) and shows robust trust in formal financial services, with 44% saving and 22% borrowing formally. Mobile and internet penetration are 80% and 56%, respectively.
Uganda – 72.8%
Uganda saw moderate growth of 66% in 2021. Digital engagement is high, with 71% using digital platforms and 54% saving formally—a notable 29% borrowed from formal sources. Mobile phone ownership is at 79%, while internet access lags at 38%.
Zambia – 72.7%
Zambia recorded one of the highest jumps, from 49% in 2021, a 24-point gain. It boasts a balanced profile, with 71% of respondents making digital payments, 50% saving, and 18% borrowing. Mobile ownership is at 79%, though internet usage remains at 39%.
Gabon – 68%
Gabon rose slightly from 66%, reflecting modest fintech penetration. Digital payment use is at 67%, and 39% of adults saved formally. The country shows potential with 87% mobile phone ownership and nearly 70% internet access.
Nigeria – 63%
Nigeria’s inclusion rate rose from 45% in 2021, marking an 18-point gain. While 57% of adults carried out digital transactions and 43% saved formally, only 9% borrowed, pointing to ongoing challenges with credit access and financial trust. Mobile phone ownership is high at 84%.
Countries with the highest financial exclusion
Despite gains, several countries remain significantly excluded. In at least 10 African nations, fewer than 40% of adults have access to financial services.
At the bottom is Niger, where only 15% adults have access to a financial account, followed by Chad (21%), Madagascar (25%), and Mauritania (27%). Others are Libya (33%), Algeria (35%), Guinea (36%), Tunisia (38%), and the Gambia (38%).
While some of these countries have high mobile phone and internet penetration, they still struggle to convert usage to access. For instance, 100% of Algerians own a mobile device, and 83% use the internet.